 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> 感染症研究に使用するコア試薬
RSV |
VZV |

RABV |

Influenza |
MPXV |
HIV |
HSV |
EBV |
NiV |
HeV |
EBOV |
ZIKV |
DENV |
SFTSV |
Coronavirus |
Rotavirus |
Coxsackievirus |
HCMV |
MuV |
hMPV |

JEV |
>>> SARS-CoV-2関連製品:COVID-19ワクチン開発&研究用の抗原 , 診断キット開発用の抗原と抗体 , SARS-CoV-2検出キット, 偽ウイルス中和アッセイサービス
>>> フォーカス製品: Hemagglutinin (HA), Neuraminidase (NA)
>>> フォーカス製品: Glycoprotein, Anti-RABV glycoprotein antibody
>>> フォーカス製品: Glycoprotein
>>> フォーカス製品: gp41, gp120, Capsid protein p24, HLA-A*0201 | B2M & HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL)
>>> フォーカス製品: Glycoprotein E
>>> フォーカス製品: NS1
>>> フォーカス製品: Glycoprotein G, Fusion glycoprotein F0 (Pre-fusion, Post-fusion)
>>> フォーカス製品: Glycoprotein, Fusion glycoprotein
>>> フォーカス製品: Gn protein
>>> Hot Products: gH&gL , Glycoprotein C (HSV-2), Glycoprotein D (HSV-1), Glycoprotein D (HSV-2), Glycoprotein E (HSV-2), post-gB
>>> Hot Products: gp350, Glycoprotein H & Glycoprotein L (EBV), Glycoprotein B (EBV)
>>> Hot Products: Pre-Fusion glycoprotein, Glycoprotein (NiV, HeV), ephrinB2
>>> Hot Products: Envelope protein, NS1
>>> Hot Products: VP4
>>> Hot Products: VP0
>>> Hot Products: Glycoprotein B / gB, gH&gL&gO:
>>> Hot Products: HN protein, Fusion glycoprotein F0, Mumps virus HN
>>> Hot Products: Post-Fusion glycoprotein F0
>>> Hot Products: Envelope protein E (JEV)
![]() HEK293による発現:タンパク質の構造は自然なコンフォメーションに近いです;
HEK293による発現:タンパク質の構造は自然なコンフォメーションに近いです;
![]() DS-PAGEとMALSによって検証された高純度;
DS-PAGEとMALSによって検証された高純度;
![]() 抗原抗体または抗原受容体結合試験によって検証された高い生物活性;
抗原抗体または抗原受容体結合試験によって検証された高い生物活性;
![]() 高い免疫原性:より高い抗体力価を誘発できます;
高い免疫原性:より高い抗体力価を誘発できます;
![]() 薬物スクリーニングやワクチン開発に適しています。
薬物スクリーニングやワクチン開発に適しています。
RSV
influenza
VZV
MPXV
HIV
RABV
HSV
NiV
HeV
ZIKV
DENV
SFTSV
EBV
EBOV
Rotavirus
Coxsackievirus
LCMV
Vaccinia Virus
HCMV
hMPV
JEV
HPV
MuV
RV
HTNV
TBEV
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
| product type | molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
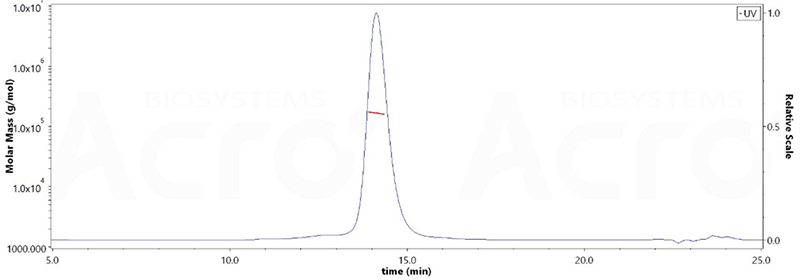
The purity of HRSV (A) Fusion glycoprotein F0, His Tag (Cat. No. RSF-V52H6) is more than 95% verified by SDS-PAGE and 90% and verified by SEC-MALS. The molecular weight of this protein is around 148-182kDa.
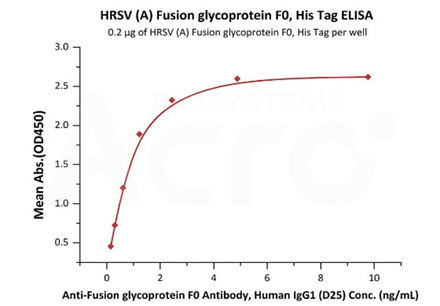
Immobilized HRSV (A) Fusion glycoprotein F0, His Tag (Cat. No. RSF-V52H7) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Anti-Fusion glycoprotein F0 Antibody, Human IgG1 (D25) with a linear range of 0.2-1 ng/mL (QC tested).
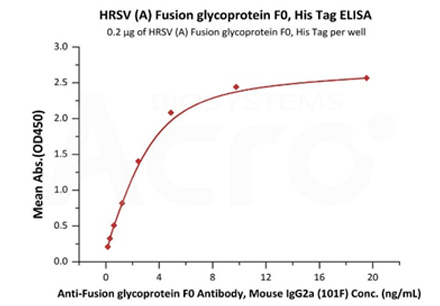
Immobilized HRSV (A) Fusion glycoprotein F0, His Tag (Cat. No. RSF-V52H7) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Anti-Fusion glycoprotein F0 Antibody, Mouse IgG2a (101F) with a linear range of 0.2-5 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
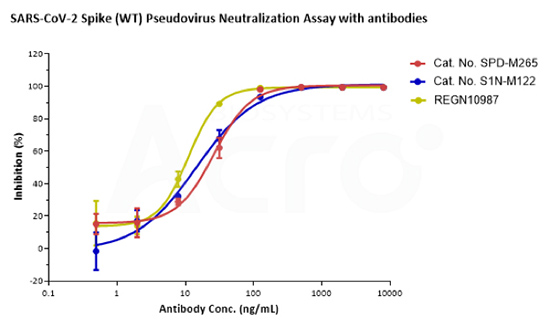
Loaded Monoclonal Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody, Mouse IgG1 (Cat. No. SPD-M305) on AMC Biosensor, can bind SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) (Cat. No. SPD-C522e) with an affinity constant of 9.07 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e).
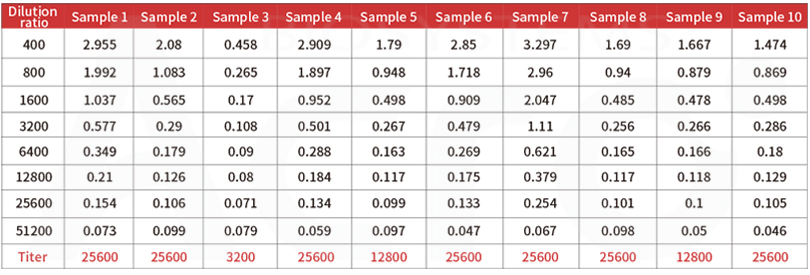
Post-vaccination serum samples are tested with Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody IgG Titer Serologic Assay Kit (Spike RBD) (Cat. No.RAS-T024), which accurately and precisely measure antibody titer in serum (Accuracy≤±15%; Intra-assay precision<10%; Inter-assay precision <15%).
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.